| UW MSK Resident Projects |
|
|
|
|
Osteoid OsteomaPrint-friendly version of this pagePosted by egensch@u.washington.edu, 3/2/04 at 1:51:10 PM.
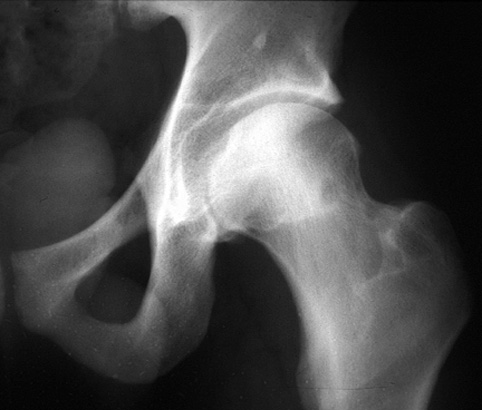
OSTEOID OSTEOMA Benign osteoblastic (bone forming) tumor. It consists of a highly vascularized osteoid core. The growing core induces a peripheral zone of sclerosis and periosteal reaction. Clinical Presentation: The hallmark is pain which is classically increased at night and often relieved by low doses of salicylates.Typically occurs in patients age 5-25 years old. Can also occur in the very young and very old. Male to female ratio is 3:1. Imaging Findings: Classic plain film/CT description: Centrally located oval or round nidus, < 2 cm in diameter, with a uniform peripheral zone of sclerosis. Unfortunately, appearance can be highly variable because the nidus can be located in the cortex, intrameduallary space, or periosteum of a bone. Description above is classic for an intracortical lesion. Diagnosis can also be more difficult when there is intraarticular extension or occurs in the spine. Additional pearls:
Examples/Pointers: Plain film imaging is the initial study in evaluating patients with suspected osteiod osteoma. Classic plain film appearance.
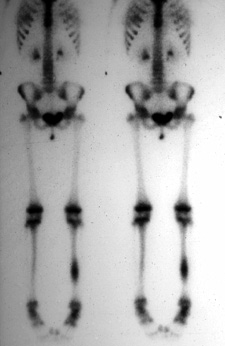
CT is preferred study for identifying and counting niduses. Classic CT appearance. 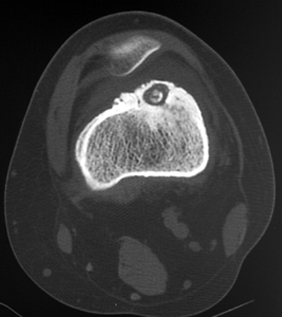 Focus of increased radiotracer uptake on bone scan (very hot). Classic bone scan appearance.
Nidus shows dense blush on angiography. Reactive bone marrow edema on MRI. Differential Diagnosis: The classically described intracortical lesion is almost an Aunt Minnie. However, since these lesions may occur in the intramedullary space or periosteum as well, the appearance can be highly variable. Sometimes all that can be seen on plain film is extensive sclerosis. Consider differential diagnoses for bone forming tumors, sclerotic lesions, bone lesions with radiolucent centers, and periosteal reaction. Consider including infection in the differential. Remember that these usually occur in 5-25 year old patients. Ask if the patient has pain. Narrow the list based on specific clinical information and imaging findings. Often the differential diagnosis includes:
Osteoblastomas: Rare, can be expansile, either lytic or > 2 cm in diameter-- in which case called a giant osteoid osteoma, have variable sclerosis, and frequently located in the posterior elements of spine. Osteoid osteoma: common, not expanisle, < 2cm in diameter, always has peripheral sclerosis, and frequently located in femur/tibia.
Treatment: Currently, preferred method of treatment is percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. Percutaneous thermal ablation is an alternative. These methods are especially preferred in difficult to reach areas. Traditional method was surgical excision and is still used in some cases. Failure to remove entire lesion leads to recurrence. References:
|
|