| UW MSK Resident Projects |
|
|
|
|
Musculoskeletal Manifestations of Sickle Cell DiseasePrint-friendly version of this pagePosted by hilla@u.washington.edu, 8/27/04 at 10:19:56 AM.
History Chwechweechw, ahotutuo, nwiiwii, and nuidudui are names the native Africans have for centuries called sickle cell disease. The disease has persisted in realatively high incidence among this population because of its "protective" effect against malarial parasite infection. Although individuals with the sickle cell gene are not immune to infection, they are afforded an advantage at resisting serious illness. Invasion by the merozoites of the red cells of individuals with sickle cell disease or trait causes sickling of the cells which triggers their destruction in the spleen before the parasite can gain access to the systemic circulation. In 1910, Dr. James Harrick described a patient from the West Indies with anemia, whose red cells were "sickle shaped," and thus introducing the western hemisphere this unique hemoglobinopathy. Etiology A point mutation of the B-globin gene produces a missense mutation yielding a substation of valine for glutamine at the 6th codon and the production of Hemoglobin S. Hemoglobin S in the deoxygenated state undergoes aggregation and polymerization with in the red cell, leading to the sickle formation of the cell membrane along with problems of cell volume regulation and endothelial adhesion. Sickle cell disease is autosomal recessive. In the individual with homozygous HbS, sickling causes severe organ damage and reduces life expectancy here in the United States to less than 50 years. Eight to ten percent of African-Americans carry the trait, and 0.2% of this population is affected by the disease. Pathophysiology The primary pathological results of this hemoglobinopathy are hyperbilirubinemia, anemia, and vaso-cclusive disorders. The latter two, along with their sequelae, are of most importance when considering musculoskeletal radiographic features of the disease. Chronic Anemia
Acute anemia and Vaso-Occlusive Disorders
Radiographic findings Marrow Hyperplasia Any anemic state has the potential to cause persistent red marrow in abnormal locations. Sickle cell patients retain the majority of their marrow as red cell forming, and in severe cases even the commonly fatty marrow epiphysis may be involved. The systemic oxygen requirement may also cause expansion of existing red marrow, leading to enlargement of marrow spaces. As with persistant red marrow, this is a finding common to any severe chronic anemic state. The classic manifestation is the "hair on end" appearance and widening of the outer table of the skull by expansion of marrow in the diploic space seen on radiography and MR. The following four MR images demonstrate extensive marrow
hemosiderosis, AVN of the right hip and both knees, and bone infarcts
in
both femurs. 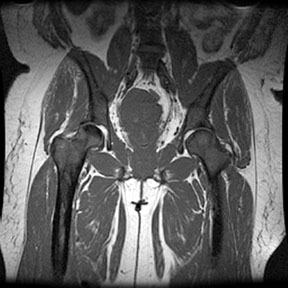 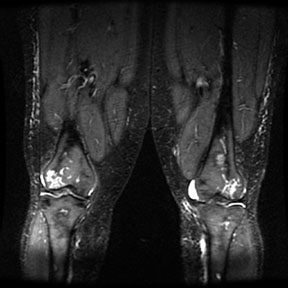 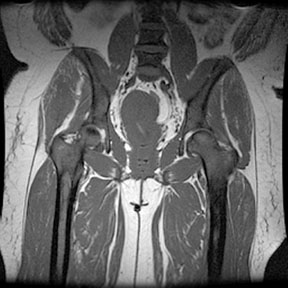 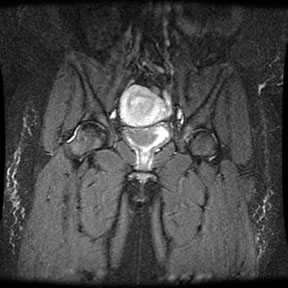 Bone Infarction Flow patterns in the marrow predispose it to infarction. The slowing of blood flow through the marrow space allows for regional hypoxia and thus sickling of red cells, leading to infarction. The proximal epiphysis of long bones, especially the humerus and femer is the most common location of infarction in sickle cell patients. Vertebral osteonecrosis and the formation of "fish vertebrae" is a classic finding. The most significant consequence of infaction is osteonecrosis. Osteonecrosis during childhood can lead to abnormal development, and during adulthood it may cause osteoarthritis or joint distruction. Age, the presence of leg ulcers, previous ostyeonecrosis of the humeral or femoral head, and higher hemoglobin levels all raise the risk of developing osteonecrosis.
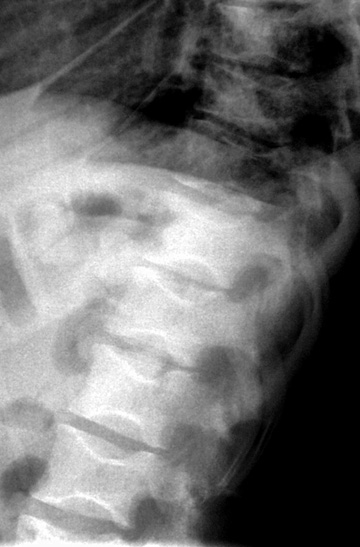
Osteonecrosis and collapse of multiple thoracic vertebral end plates, giving the appearance of "fish vertebrae" in this 28 year old woman with sickle cell disease and recurrent bone pain.
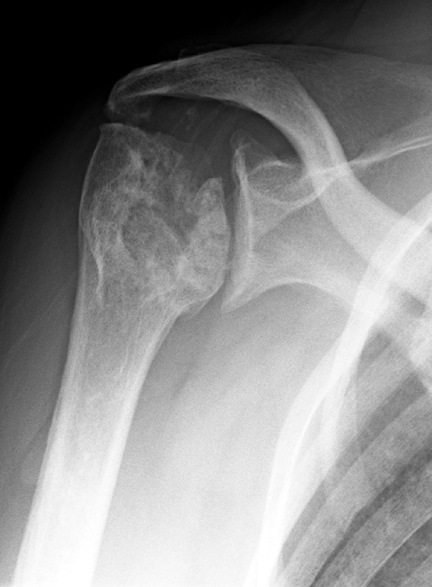
Humeral head infarction and osteonecrosis in a 50 year old female with sickle cell disease.
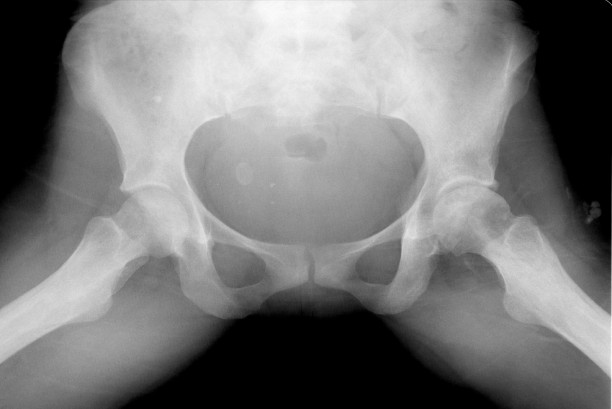
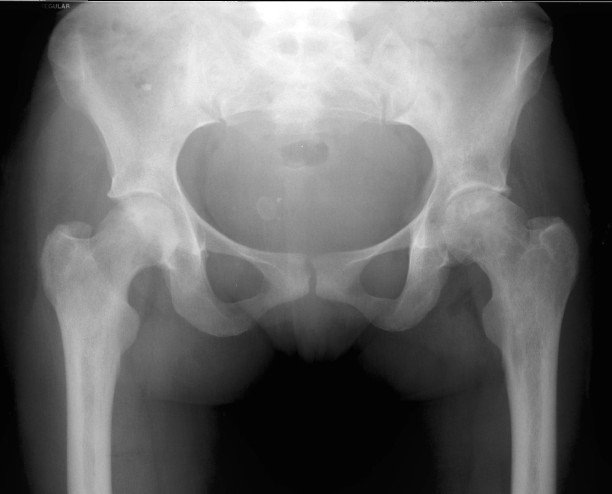
Films of a 38 year old female with bilateral hip pain showing bilateral femoral head infarcts and osteonecrosis with subchondral collapse of the superior femoral articular surface. Osteomyelitis Individuals with sickle cell disease are predisposed to osteomyelitis secondary to ischemic injury of both bone and GI tract. This results in a high incidence of seeding of infarct beds with GI flora, most commonly Salmonela; as opposed to the more common cause of osteomyelitis in the general population, S. aureus. Osteomyelitis is difficult to distinguish from bone infarction, and occurs much less commonly. Findings on plain film are nonspecific and include periostitis and osteopenia. MR is the preferred method for evaluation and demonstrates high signal on T2 weighted images and STIR. The most sensitive study is a T1 fat saturation study performed post gadolinium. Abnormal enhancement in this series is indicative of infection. References
|
|