| Home | Frontal | Maxillary | Ethmoid: Normal | Ethmoid: Abnormal | Sphenoid | Interactive Atlas | Quiz |
Ethmoid Sinus: Normal Anatomy & Variants |
|
The ethmoid sinus can have a variable number of air cells. Additionally, the ethmoid sinuses are divided into groups of cells by bony basal lamellae. The most imporant one is the basal lamellae of the middle turbinate which separates the ethmoid into anterior and posterior groups with different drainage patterns.
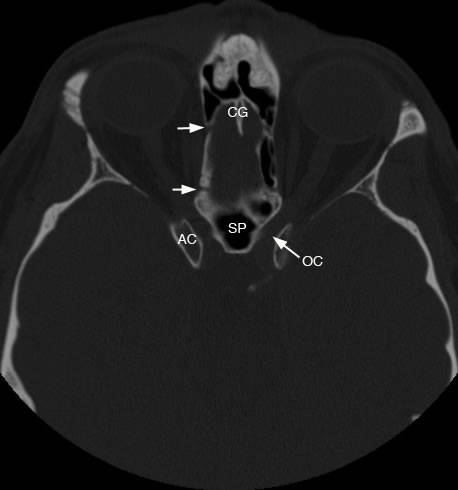
Axial view shows small arrows demonstrating bony canal for anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries (CG: crista galli, AC: anterior clinoid process, OC: optic canal, SP: sphenoid sinus).
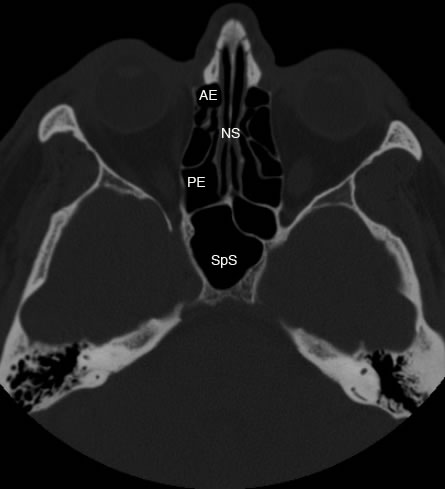
Axial image showing normal ethmoid sinus anatomy. Arrows point to the lateral attachment of the basal lamellae to lamina papyracea separating anterior and posterior ethmoid sinuses (AE: anterior ethmoid, PE: posterior ethmoid, NS: nasal septum, SpS: sphenoid sinus)
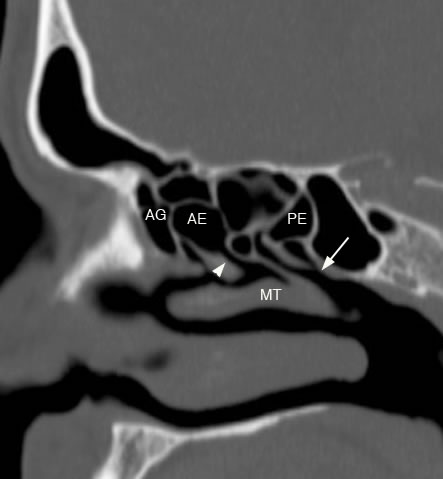
Sagittal image with arrowhead demonstrating anterior ethmoid drainage to hiatus semilunaris and middle meatus. Arrow showing posterior ethmoid drainage to sphenoethmoidal recess and superior meatus. (AG: agger nasi cell, AE: anterior ethmoid, PE: posterior ethmoid, MT: middle turbinate)
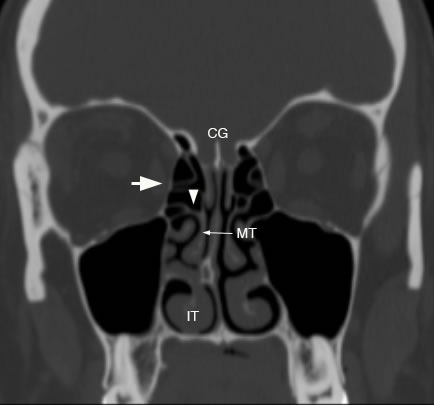
Coronal image with arrowhead showing lateral attachment of basal lamellae to lamina papyracea marked by the arrow. (CG: crista galli, *: cribriform plate, FE: fovea ethmoidalis, MT: middle turbinate, IT: inferior turbinate)
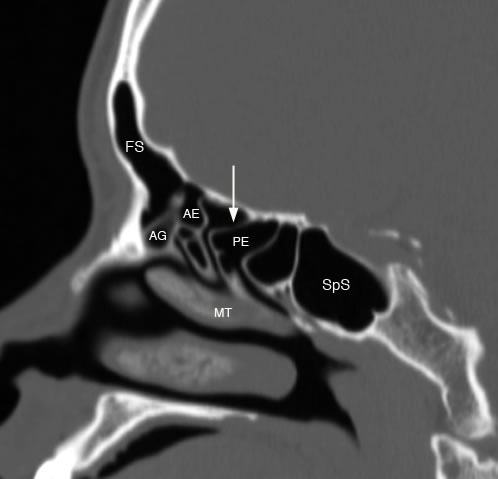
Sagittal image with arrow showing vertical attachment of basal lamellae to anterior skull base separating the anterior ethmoid (AE) and posterior ethmoid (PE) sinuses. (FS: frontal sinus, AG: agger nasi cell, SpS: sphenoid sinus, MT: middle turbinate)
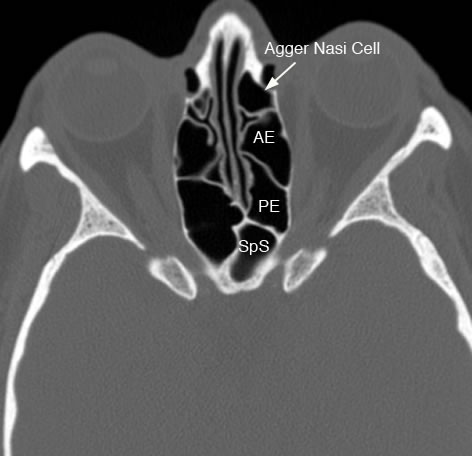
Axial image demonstrating an Agger Nasi air cell which is the most anterior ethmoid air cell. (AE: anterior ethmoid, PE: posterior ethmoid, SpS: sphenoid sinus)
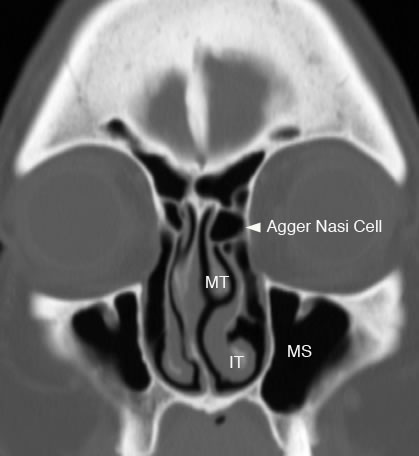
Coronal image with arrowhead showing Agger Nasi air cell. (MS: maxillary sinus, MT: middle turbinate, IT: inferior turbinate)
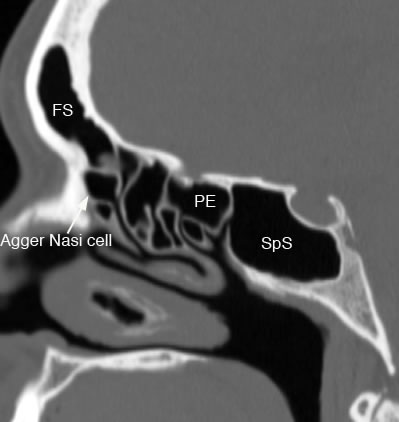
Sagittal image shows Agger Nasi air cell. (FS: frontal sinus, PE: posterior ethmoid, SpS: sphenoid sinus)
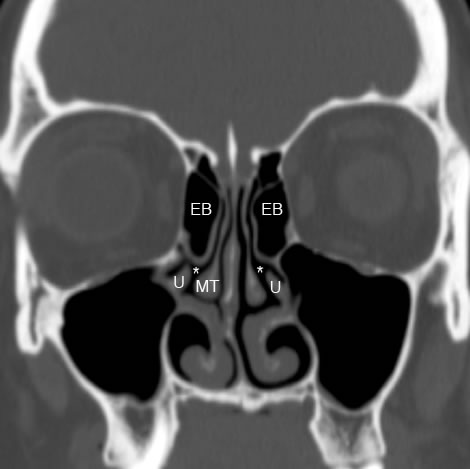
Coronal image shows ethmoid bulla air cells superior to uncinate processes. The (*) highlight the hiatus semilunaris. Ethmoid bulla air cells are part of the anterior ethmoid sinuses and make up the superior border of the hiatus semilunaris. (EB:ethmoid bulla, U: uncinate process, MT: middle turbinate)
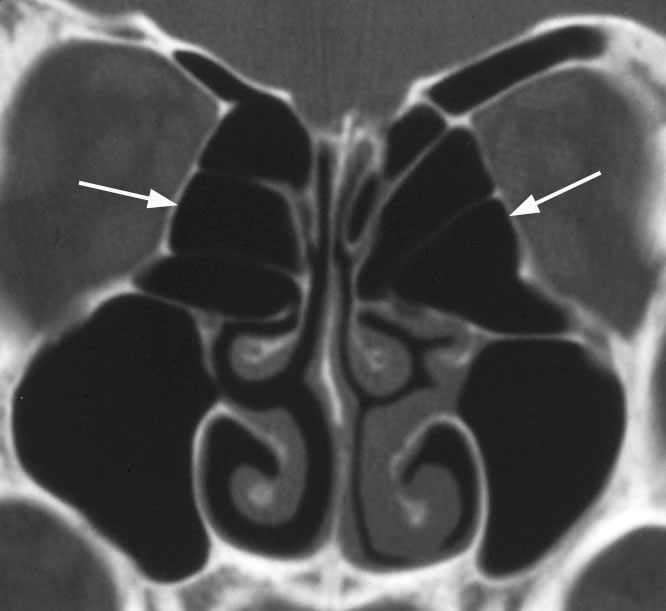
Coronal image with arrows pointing to enlarged ethmoid bulla encroaching on the OMU. Ethmoid bulla air cells can demonstrate variable pneumatization.
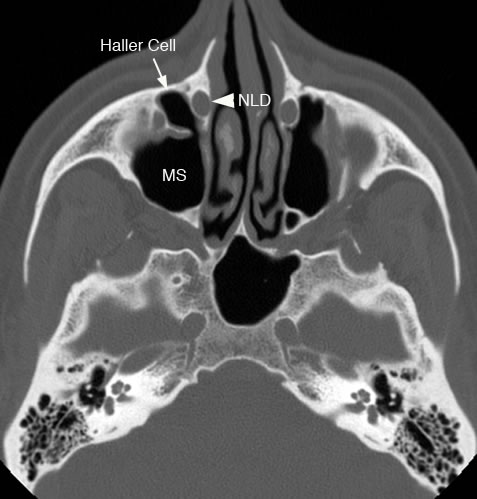
Axial image with arrow pointing to an infraorbital ethmoid air cell (Haller cell). If present, a Haller cell can cause narrowing of the infundibulum and maxillary sinus ostuim potentially causing obstruction. (MS: maxillary sinus, NLD: nasolacrimal duct)
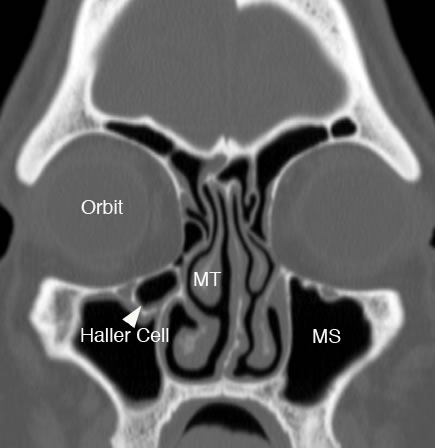
Coronal image with arrowhead pointing to infraorbital ethmoid air cell ( Haller cell) which is narrowing the maxillary sinus ostium and infundibulum. (MT: middle turbinate, MS: maxillary sinus)
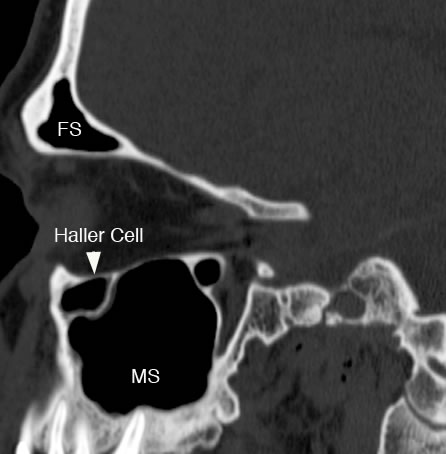
Sagittal image with arrowhead pointing to infraorbital ethmoid air cell (Haller cell). (FS: frontal sinus, MS: maxillary sinus) |